

바이오스 업데이트 했더니 윈도우즈 부팅화면에 MSI 로고가 나왔다. 윈도우즈 옵션인가 싶어서 검색했는데 예상외로 메인보드 옵션을 수정해줘야 했다.
컴퓨터 부팅할 때 메인보드 설정으로 들어가서 Settings\Boot 에 있는 Full Screen Logo Display 를 Disable 로 바꿔주면 된다.


바이오스 업데이트 했더니 윈도우즈 부팅화면에 MSI 로고가 나왔다. 윈도우즈 옵션인가 싶어서 검색했는데 예상외로 메인보드 옵션을 수정해줘야 했다.
컴퓨터 부팅할 때 메인보드 설정으로 들어가서 Settings\Boot 에 있는 Full Screen Logo Display 를 Disable 로 바꿔주면 된다.
python 스크립트를 배포할 때 스크립트 실행환경 구축 안내하는게 번거롭다. 실행파일 형태로 배포한는게 편하다. 특히 파일 하나로 배포될 수 있다면 제일 좋다.
https://pyinstaller.org/en/stable/operating-mode.html#bundling-to-one-file
PyInstaller 를 사용하면 간단하게 실행파일로 만들 수 있다.
> pyinstaller script.pypyinstaller 를 설치하고 위와 같이 실행하면 한 폴더에 배포파일이 생성된다.
> pyinstaller --onefile script.py파일 하나로 만들고 싶으면 --onefile 이나 -F 옵션을 사용하면 된다.
$ pwdx -h
Usage:
pwdx [options] pid...
Options:
-h, --help display this help and exit
-V, --version output version information and exit
For more details see pwdx(1).프로세스 실행경로를 /proc/[PID]/exe 를 통해 찾아볼 수도 있지만 pwdx 를 이용하면 더 간편하다.
$ ps -aux
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1 0.0 0.0 2456 1596 hvc0 Sl+ 23:24 0:00 /init
root 4 0.0 0.0 2472 196 hvc0 Sl+ 23:24 0:00 plan9 --control-socket 5 --log-level 4 --server-fd 6 --
root 8 0.0 0.0 2460 112 ? Ss 23:25 0:00 /init
root 9 0.0 0.0 2476 116 ? S 23:25 0:00 /init
xxx 10 0.0 0.0 10044 5004 pts/0 Ss 23:25 0:00 -bash
xxx 96 0.0 0.0 10860 3428 pts/0 R+ 23:27 0:00 ps -aux
$ pwdx 10
10: /home/xxxps 로 PID 를 알아낸 다음 pwdx [PID] 를 입력하면 실행경로가 보인다. 권한이 필요한 경우 sudo pwdx [PID] 같은 식으로 입력하면 된다.
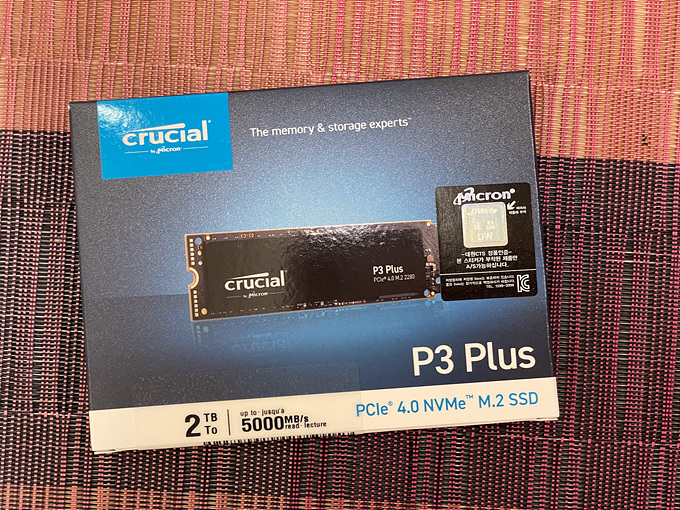




요새 핫딜로 제일 많이 뜨는 상품이 ssd 다. 최고 성능 제품은 아니지만 2T 제품이 99,000 원에 살 수 있었다.
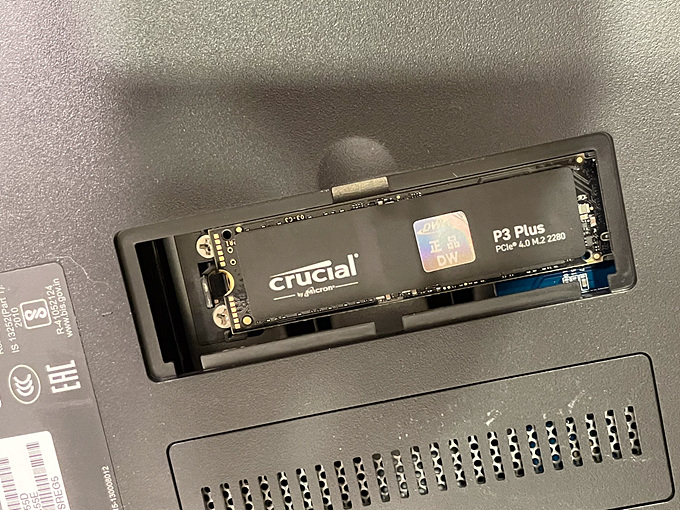


923+ 는 nvme ssd 를 볼륨으로 사용할 수 있지만 920+ 는 캐시로만 설정 가능했다. 하지만 수동으로 볼륨으로 설정 가능하다고 해서 구매한 ssd 를 920+ 에 설치했다.
https://academy.pointtosource.com/synology/synology-ds920-nvme-m2-ssd-volume/
위 사이트 내용을 참고했다. nvme ssd 설치하고 ssh 로 접근해 device 를 설정 후 볼륨 관리자에서 활성화 시키는 방식이다.
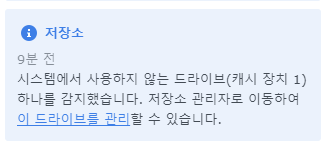

nvme ssd 설치 후 부팅하면 장치가 인식되었다는 알림이 뜨고 저장소 관리자에서 확인할 수 있다.

DSM 7.2 사용 중인데 혹시나 바로 스토리지 풀을 생성할 수 있나 싶었지만 지원하지 않았다.
1. ls /dev/nvme* (Lists your NVMe drives)
2. sudo -i (Type this, then type your password for Super User)
3. fdisk -l /dev/nvme0n1 (Lists the partitions on NVMe1)
4. fdisk -l /dev/nvme1n1 (Lists the partitions on NVMe2)
5. synopartition --part /dev/nvme0n1 12 (Creates the Syno partitions on NVMe1)
6. synopartition --part /dev/nvme1n1 12 (Creates the Syno partitions on NVMe2)
7. fdisk -l /dev/nvme0n1 (Lists the partitions on NVMe1)
8. fdisk -l /dev/nvme1n1 (Lists the partitions on NVMe2)
9. cat /proc/mdstat (Lists your RAID arrays/logical drives)
10. mdadm --create /dev/md3 --level=1 --raid-devices=2 --force /dev/nvme0n1p3 /dev/nvme1n1p3 (Creates the RAID array RAID 1 --level=1 RAID 0 --level=0)
11. cat /proc/mdstat (Shows the progress of the RAID resync for md3 or md4)
12. echo 0 > /sys/block/md3/queue/rotational
13. mkfs.btrfs -f /dev/md3 (Formats the array as btrfs)ssh 로 접근해 파티션을 만들고 raid 생성 후 포맷을 해주면 된다.
# cat /proc/mdstat
Personalities : [raid1] [raid6] [raid5] [raid4] [raidF1]
md6 : active raid5 sata7p8[0] sata5p8[3] sata9p8[2] sata8p8[1]
17581508736 blocks super 1.2 level 5, 64k chunk, algorithm 2 [4/4] [UUUU]
md5 : active raid5 sata5p7[5] sata9p7[4] sata8p7[3] sata7p7[2] sata6p7[1]
5860475648 blocks super 1.2 level 5, 64k chunk, algorithm 2 [5/5] [UUUUU]
md2 : active raid6 sata3p3[0] sata1p3[3] sata2p3[2] sata4p3[1]
5850889088 blocks super 1.2 level 6, 64k chunk, algorithm 2 [4/4] [UUUU]
md7 : active raid1 sata9p9[0] sata5p9[1]
3904854208 blocks super 1.2 [2/2] [UU]
md4 : active raid5 sata5p6[6] sata9p6[5] sata8p6[4] sata7p6[3] sata6p6[2]
703225088 blocks super 1.2 level 5, 64k chunk, algorithm 2 [5/5] [UUUUU]
md3 : active raid5 sata5p5[7] sata7p5[4] sata8p5[5] sata9p5[6] sata6p5[3]
1230960384 blocks super 1.2 level 5, 64k chunk, algorithm 2 [5/5] [UUUUU]
md1 : active raid1 sata3p2[0] sata1p2[3] sata2p2[2] sata4p2[1]
2097088 blocks [4/4] [UUUU]
md0 : active raid1 sata3p1[0] sata1p1[3] sata2p1[2] sata4p1[1]
2490176 blocks [4/4] [UUUU]
unused devices: <none>1. cat /proc/mdstat 을 통해 추가할 md# 을 확인하자. 순서대로 있는 줄 알고 md7을 추가하면 될거라고 생각했는데 md7 이 사이에 있었다.
# fdisk -l /dev/nvme0n1
Disk /dev/nvme0n1: 1.8 TiB, 2000398934016 bytes, 3907029168 sectors
Disk model: CT2000P3PSSD8
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
# synopartition --part /dev/nvme0n1 12
Device Sectors (Version6: SupportRaid)
/dev/nvme0n11 4980087 (2431 MB)
/dev/nvme0n12 4192965 (2047 MB)
Reserved size: 257040 ( 125 MB)
Primary data partition will be created.
WARNING: This action will erase all data on '/dev/nvme0n1' and repart it, are you sure to continue? [y/N] y
Cleaning all partitions...
Creating sys partitions...
Creating primary data partition...
Please remember to mdadm and mkfs new partitions.nvme1 장비에 파티션을 설정하자.
# mdadm --create /dev/md8 --level=0 --raid-devices=1 --force /dev/nvme0n1p3
mdadm: Defaulting to version 1.2 metadata
mdadm: array /dev/md8 started.생성된 파티션으로 raid 를 생성하자.
# mdadm --create --help
Usage: mdadm --create device -chunk=X --level=Y --raid-devices=Z devices
This usage will initialise a new md array, associate some
devices with it, and activate the array. In order to create an
array with some devices missing, use the special word 'missing' in
place of the relevant device name.
Before devices are added, they are checked to see if they already contain
raid superblocks or filesystems. They are also checked to see if
the variance in device size exceeds 1%.
If any discrepancy is found, the user will be prompted for confirmation
before the array is created. The presence of a '--run' can override this
caution.
If the --size option is given then only that many kilobytes of each
device is used, no matter how big each device is.
If no --size is given, the apparent size of the smallest drive given
is used for raid level 1 and greater, and the full device is used for
other levels.
Options that are valid with --create (-C) are:
--bitmap= : Create a bitmap for the array with the given filename
: or an internal bitmap is 'internal' is given
--chunk= -c : chunk size in kibibytes
--rounding= : rounding factor for linear array (==chunk size)
--level= -l : raid level: 0,1,4,5,6,10,linear,multipath and synonyms
--parity= -p : raid5/6 parity algorithm: {left,right}-{,a}symmetric
--layout= : same as --parity, for RAID10: [fno]NN
--raid-devices= -n : number of active devices in array
--spare-devices= -x: number of spare (eXtra) devices in initial array
--size= -z : Size (in K) of each drive in RAID1/4/5/6/10 - optional
--data-offset= : Space to leave between start of device and start
: of array data.
--force -f : Honour devices as listed on command line. Don't
: insert a missing drive for RAID5.
--run -R : insist of running the array even if not all
: devices are present or some look odd.
--readonly -o : start the array readonly - not supported yet.
--name= -N : Textual name for array - max 32 characters
--bitmap-chunk= : bitmap chunksize in Kilobytes.
--delay= -d : bitmap update delay in seconds.
--write-journal= : Specify journal device for RAID-4/5/6 arraySHR은 설정이 안되는 것 같다.
# echo 0 > /sys/block/md8/queue/rotational
root@nkColony:~# mkfs.btrfs -f /dev/md8
btrfs-progs v4.0
See http://btrfs.wiki.kernel.org for more information.
Detected a SSD, turning off metadata duplication. Mkfs with -m dup if you want to force metadata duplication.
Performing full device TRIM (1.81TiB) ...
Label: (null)
UUID: fc77a1e9-fce0-44ce-bcda-7825e994ac9e
Node size: 16384
Sector size: 4096
Filesystem size: 1.81TiB
Block group profiles:
Data: single 8.00MiB
Metadata: single 8.00MiB
System: single 4.00MiB
SSD detected: yes
Incompat features: extref, skinny-metadata
Number of devices: 1
Devices:
ID SIZE PATH
1 1.81TiB /dev/md8생성 후에 포맷까지 하고 재부팅을 한다.

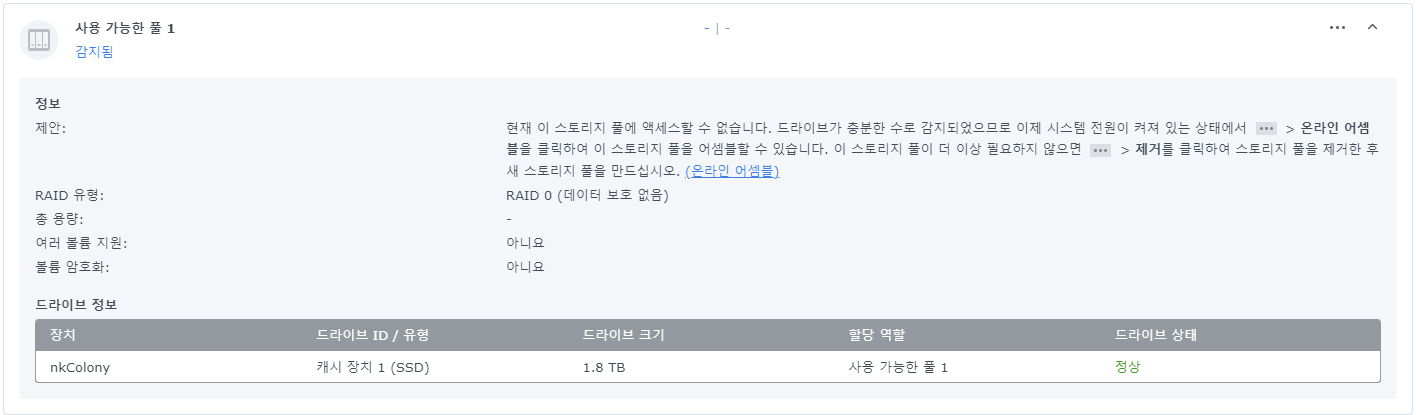
사용 가능한 풀이 감지되었고 알림이 뜨고 저장소 관리자에서 사용 가능한 풀로 표기된다.
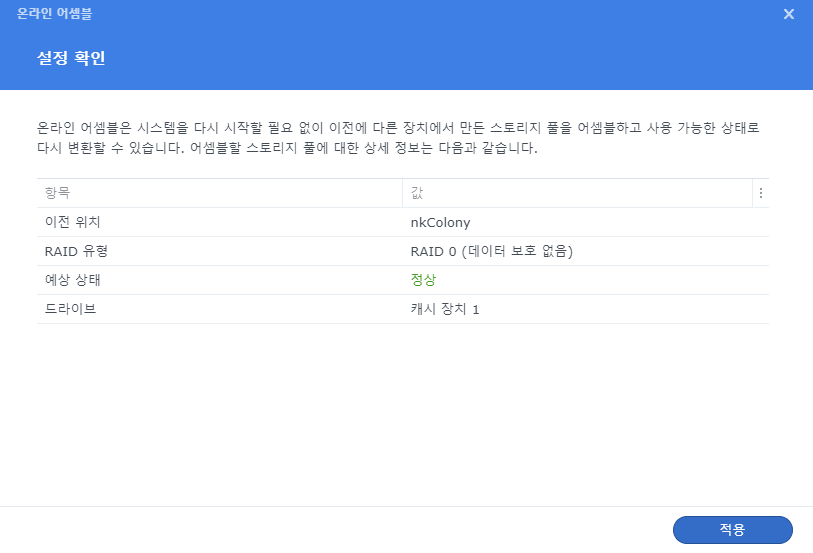

오른쪽에 있는 ... 메뉴에서 온라인 어셈블을 선택하면 스토리지 풀이 추가된다.
여유 장비가 없어서 추가 설정이 가능한지 모르겠지만 일단은 스토리지 풀로 추가해서 사용하고 있다. 기존 스토리지 풀에 추가하거나 할 수는 없었고 nvme ssd 를 볼륨으로 사용할 수 있다 정도 수준이다.
절전 상태에서 복귀할 때 하드 소리 때문에 시끄럽고 버벅거리는데 ssd 로 바뀐다면 소음이 줄어들 것 같은 기대가 있다.
(2023-07-30) 디스크 디비 업데이트 되었다고 재부팅했더니 지원하지 않는 디스크라는 메시지가 보인다. :(
# mdadm --assemble --scan
mdadm: /dev/md/8 has been started with 1 drive.ssh 로 접근해서 mdadm 으로 재설정해봤지만 재부팅하면 날라가버렸다. :(
https://svrforum.com/nas/824972
서버포럼 - DSM 7.2-64570 이후 캐시장치 - 현재 DSM버전에서 지원되지 않습니다 에러 => 해결
글 지울까 하다가 이미 읽으신 분이 몇분 계셔서, 해결법만 추가하고 글 남겨둡니다. /etc.defaults/synoinfo.conf 의 support_m2_pool="no" 를 support_m2_pool="yes" 로 바꾸고 재부팅 하면 됩니다. (재부팅은 왜이..
svrforum.com
'지원하지 않는 디스크' 라는 메시지를 검색해보니 업데이트 때 발생할 수 있나 보다.
# vi /etc.defaults/synoinfo.conf설정 파일을 열어서 support_m2_pool 이라는 설정을 yes 바꾸고 재부팅하자.
support_m2_pool="yes"

저장소 관리자에서 m.2 장치가 캐시가 아닌 드라이브로 잡히면서 오류가 수정되었다. m.2 ssd 추가로 사서 묶어서 사용하려고 했는데 언제 막힐지 몰라서 temp 용도로만 써야겠다.
집 모니터는 QHD, WFHD 인데 회사 모니터는 FHD 라 불편했다.

NVIDIA 그래픽 카드를 사용중이라면 제어판에서 지원하는 해상도 보다 더 높은 해상도를 사용할 수 있다.

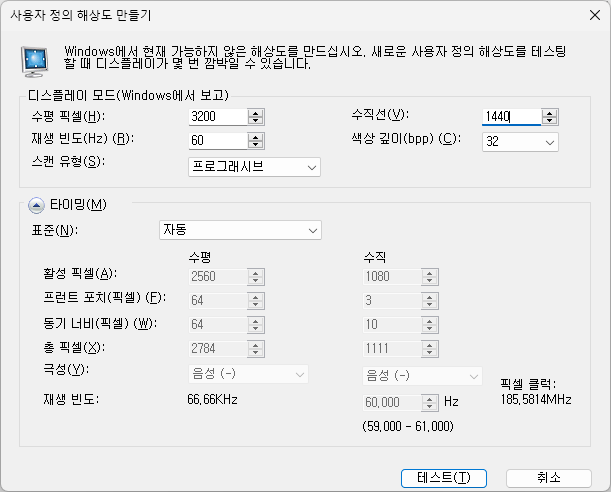
사용자 정의 해상도 만들기를 눌러 QHD+ 를 만들었다.


테스트를 누르면 해상도 변경 확인창이 뜨고 예를 누르면 사용자 정의가 추가된 것을 확인할 수 있다.

디스플레이 설정 해상도에 3200 x 1440 이 추가되어 있다.
지원하지 않는 해상도라 가독성은 떨어지지만 넓은 해상도가 필요하다면 어쩔 수 없다.
AMD 계열은 가상초고해상도 라는 옵션이 있나보다. 인텔도 옛날 모델에는 있었는데 최근 버전에는 찾을 수가 없었다.
c# 에서 객체를 json 문자열로 바꾸려면 System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer 를 사용하면 된다.
using System.Text.Json;
public class ObjectA
{
public int a { get; set; }
public int b { get; set; }
public int c { get; set; }
}
public class JsonTest
{
public static void Main()
{
var objA = new ObjectA() { a = 1, b = 2, c = 3};
var jsonStr = System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.Serialize(objA);
Console.WriteLine(jsonStr);
}
}
$ JsonTest.exe
{"a":1,"b":2,"c":3}위와 같이 json 문자열로 변환되기를 원하는 문자열을 property 로 선언하고 JsonSerializer.Serialize 함수를 호출하면 된다.
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using System.Text.Json;
public class ObjectA
{
public int a { get; set; }
public int b { get; set; }
public int c { get; set; }
public int d;
}
public class JsonTest
{
public static void Main()
{
var objA = new ObjectA() { a = 1, b = 2, c = 3, d = 4 };
var jsonStr = System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.Serialize(objA);
Console.WriteLine(jsonStr);
var jsonStr2 = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(objA);
Console.WriteLine(jsonStr2);
}
}$ JsonTest.exe
{"a":1,"b":2,"c":3}
{"d":4,"a":1,"b":2,"c":3}하지만 위와 같이 property 선언되지 않은 멤버들은 json 문자열로 출력되지 않는다. property 선언되지 않은 d 까지 json 문자열로 변환되길 바란다면 Newtonsoft.Json 을 이용하자. JsonConvert.SerializeObject 함수를 이용하면 된다.
참고로 protobuf descriptor 가 없는 경우에 System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer 를 이용한다면 json 으로 변환되지 않았다.
참고 : https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6201529/how-do-i-turn-a-c-sharp-object-into-a-json-string-in-net
How do I turn a C# object into a JSON string in .NET?
I have classes like these: class MyDate { int year, month, day; } class Lad { string firstName; string lastName; MyDate dateOfBirth; } And I would like to turn a Lad object into a...
stackoverflow.com
https://www.mongodb.com/json-and-bson
JSON And BSON
Learn how MongoDB uses the lightweight and flexible BSON, an extension JSON, to maximize efficiency for programming languages
www.mongodb.com
bson 은 mongodb 에서 나온 개념인데 "binary JSON" 이다.
{"hello": "world"} →
\x16\x00\x00\x00 // total document size
\x02 // 0x02 = type String
hello\x00 // field name
\x06\x00\x00\x00world\x00 // field value
\x00 // 0x00 = type EOO ('end of object')
{"BSON": ["awesome", 5.05, 1986]} →
\x31\x00\x00\x00
\x04BSON\x00
\x26\x00\x00\x00
\x02\x30\x00\x08\x00\x00\x00awesome\x00
\x01\x31\x00\x33\x33\x33\x33\x33\x33\x14\x40
\x10\x32\x00\xc2\x07\x00\x00
\x00
\x00txt 기반의 json 을 변형해서 binary 형식으로 serialize 했다.
https://bsonspec.org/spec.html
BSON (Binary JSON): Specification
BSON is a binary format in which zero or more ordered key/value pairs are stored as a single entity. We call this entity a document. The following grammar specifies version 1.1 of the BSON standard. We've written the grammar using a pseudo-BNF syntax. Vali
bsonspec.org
network protocol 정의할 때 보던 형식과 유사하다.

위와 같은 폴더들이 있을 때 one 으로 시작하는 폴더들에 대해 어떤 작업을 처리하고 싶다면 FOR /D 를 사용한다.
for /D [/r] %%parameter IN (folder_set) DO command>for /D %i in ("one*") do @echo %~nxi
oneapi-tbb-2021.5.0-win
oneTBB-2021.5.0출처 : https://ss64.com/nt/for_d.html
for /d - Loop through directory - Windows CMD - SS64.com
Conditionally perform a command on several Directories/Folders. In all cases for /d will start searching from the current directory. Read the main FOR introduction page for a full description of assigning the replaceable %%parameter. FOR parameters are use
ss64.com
CentOS 에서는 패키지 관리를 위해 yum 을 사용한다.
$ yum list | grep nginx
pcp-pmda-nginx.x86_64 4.3.2-13.el7_9 updates
$ yum search nginx
Loaded plugins: fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* base: mirror.kakao.com
* extras: mirror.kakao.com
* updates: mirror.kakao.com
================================================== N/S matched: nginx ==================================================
pcp-pmda-nginx.x86_64 : Performance Co-Pilot (PCP) metrics for the Nginx Webserver
Name and summary matches only, use "search all" for everything.패키지 목록 조회는 yum list 나 yum search를 사용한다.
$ yum install pcp-pmda-ngnix설치는 yum install 을 사용한다.
$ yum update pcp-pmda-nginx업데이트는 yum update 를 사용한다.
출처 : https://security-log.tistory.com/24
YUM 명령어 사용법 (설치, 삭제, 업데이트, 설치 가능 패키지 조회, 설치된 패키지 조회, 정보 보기
yum info [패키지 이름] YUM 명령어 사용법 1. 패키지 조회 (설치가능 + 설치된 패키지) 1) 명령어 yum list | grep [패키지 이름] 2) 사용예 yum list | grep nginx 2. 설치된 패키지 조회 1) 명령어 yum list installed |
security-log.tistory.com
CC=g++
CFLAGS=-c -Wall
LDFLAGS=
SOURCES=main.cpp hello.cpp factorial.cpp
OBJECTS=$(SOURCES:.cpp=.o)
EXECUTABLE=hello
all: $(SOURCES) $(EXECUTABLE)
$(EXECUTABLE): $(OBJECTS)
$(CC) $(LDFLAGS) $(OBJECTS) -o $@
.cpp.o:
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $< -o $@윈도우즈 환경에서 Visual Studio 로 개발하다 보니 makefile 쓰는 법을 다 까먹었다. : 기준으로 왼쪽이 target 오른쪽이 source 인 건 알겠는데 $@, $< 같은 변수는 처음 봤다.
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3220277/what-do-the-makefile-symbols-and-mean
What do the makefile symbols $@ and $< mean?
CC=g++ CFLAGS=-c -Wall LDFLAGS= SOURCES=main.cpp hello.cpp factorial.cpp OBJECTS=$(SOURCES:.cpp=.o) EXECUTABLE=hello all: $(SOURCES) $(EXECUTABLE) $(EXECUTABLE): $(OBJECTS) $(CC) $(LDFLAGS) $(
stackoverflow.com
$@ 은 왼쪽, $<은 오른쪽 첫번째, $^ 은 오른쪽 전부를 나타낸다고 한다.
all : library.cpp main.cpp위와 같은 경우 아래와 같은 값이 된다고 한다.
$@ 은 all
$< 은 library.cpp
$^ 은 library.cpp main.cpp
https://www.gnu.org/software/make/manual/html_node/Automatic-Variables.html#Automatic-Variables
Automatic Variables (GNU make)
10.5.3 Automatic Variables Suppose you are writing a pattern rule to compile a ‘.c’ file into a ‘.o’ file: how do you write the ‘cc’ command so that it operates on the right source file name? You cannot write the name in the recipe, because the
www.gnu.org